{{timelineevent.meta.fids_timeline_headline}}
{{pageContent.title.rendered | trustAsHtml}}
{{pageContent.meta.fids_top_subheading}}
{{pageContent.meta.fids_top_heading}}
Content Not Found
Apologies, but no results were found for the requested content.
Our Cart Locations
{{pageContent.meta.fids_group_title}}
{{post.date | date: 'dd MMMM yyyy'}}
Read more{{pageContent.meta.fids_top_heading}}
{{pageContent.meta.fids_top_subheading}}
Address:
10 Victoria Road, Lorenztville Johannesburg, Gauteng
Email:
info@goodbyemalaria.com
Telephone:
+27 11 216 3537
Our Airport Stores
George Airport
Domestic Departures Ground Floor
Cape Town International Airport
Domestic Departures Gate A8
OR Tambo International Airport (Landside)
2nd Floor Domestic Arrivals Food Court
OR Tambo International Airport (Airside)
Gate 7 & 8 International Departures
Address:
10 Victoria Road, Lorenztville Johannesburg, Gauteng
Email:
info@goodbyemalaria.com
Telephone:
+27 11 216 3537
Our Airport Stores
George Airport
Domestic Departures Ground Floor
Cape Town International Airport
Domestic Departures Gate A8
OR Tambo International Airport (Landside)
2nd Floor Domestic Arrivals Food Court
OR Tambo International Airport (Airside)
Gate 7 & 8 International Departures
Content Not Found
Apologies, but no results were found for the requested content.
{{pageContent.meta.fids_top_heading}}
{{pageContent.meta.fids_top_subheading}}
{{person.title.rendered}}
{{pageContent.meta.fids_top_heading}}
Contributing Partners
More Contributors & In-Kind Support
{{pageContent.meta.fids_top_heading}}
{{pageContent.meta.fids_top_subheading}}
{{faq.title.rendered}}
{{pageContent.meta.fids_top_heading}}
Malaria is a complex parasite that's evolved to be able to live in the mosquito as the vector, and in a vertebrate host, us. It invades and grows in various cell types while stealthily evading the host’s immune responses. It also goes through several life stages while in the human host, making it difficult to tackle.

1. Transmission to human (injects sporozoites via bite)
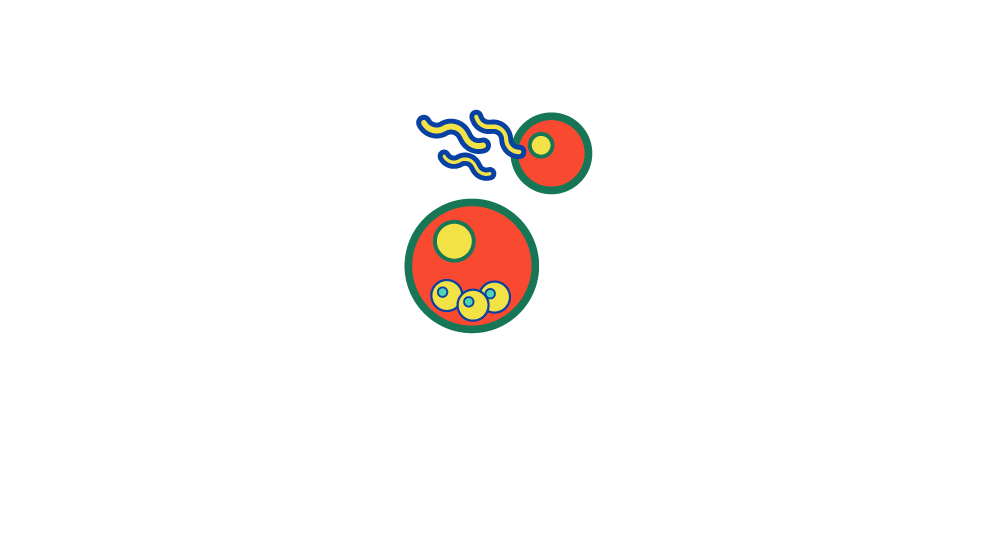
2. Sporozoites enter liver and infect hepatocytes Mitotic replication

3. Liver cells rupture and merozoites released
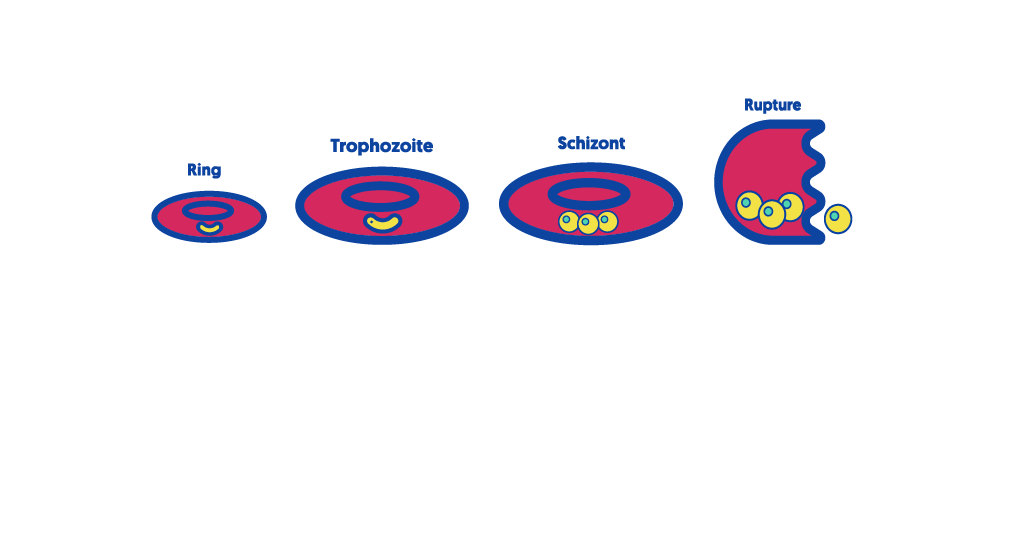
4. Intraerythrocytic cycle (asexual/ symptomatic cycle)

5. Sexual cycle (merozoites produce gametocytes instead)

6. Transmission to mosquito (ingests gametocytes via bite)

7. Gametocytes mate, undergo meiosis

8. Migrates through midgut wall forms oocyst

9. Sporozoites develop